3D SIMULATION
Gilles Schaefer is the main creator of the following software:
- CALLAS
- PROSPER
- LECOS
- TOWER
Software is a structuring element in the vehicle design process: vehicle design uses digital simulation, but software design formalizes and validates an understanding of how vehicles work.
Lap Time Simulation
TOUR performance calculation for racing cars, used by Renault Sport, Peugeot Sport, Citroën Sport, ORECA, Snobeck, Nissan Motorsport, etc.; in particular, it steered the design of the Peugeot 905 towards high aerodynamic downforce, to the detriment of top speed, which was more effective for the World Championship.
3D Vehicle Dynamics
CALLAS and PROSPER are two vehicle dynamics software packages based on 4 major ideas:
- the 3D approach is the most interesting because lateral and longitudinal vertical phenomena are not independent: for example, lifting the foot when cornering is the case that determines the understeer reserve for many vehicles, and it combines all three dynamics
- functional modeling is the most efficient way to design (delving into the details of mechanisms or mechatronics makes the design process more cumbersome)
- the simulation must be easy enough to be put on the desk of any design engineer, which implies the use of a vocabulary and trade tests, and a high-level GUI enabling analysis and dialogue (with interfacing with office automation)
- simulation must "learn from the real thing", hence the need to support on-board acquisitions in databases
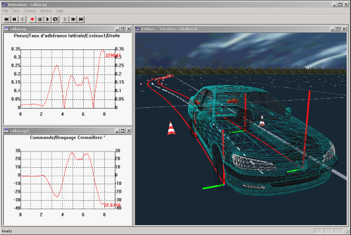

CALLAS and PROSPER are now distributed worldwide by AV SIMULATION.
Below are some videos showing interesting simulation cases.
| This test consists of driving a touring car at progressively increasing speed between pins, which becomes more and more difficult; we note the slightly understeer behavior at the start, then very oversteer with the call-counter-call effect well known in rallying, with a strong rear slip. | |
| The MODIX vehicle was developed for DGA-ETAS as a rolling laboratory for 8×8 ground links. Each wheel is equipped with independent load, traction, braking and steering capabilities. A computerized control system simulates the different configurations imagined for future 8×8s. This video was presented at the ISTVS conference in Ferrara in 1997. | |
| A research project on the stability of liquid-filled tractor+semi-trailer articulated lorries was carried out with PREDIT funding. The aim was to understand and propose improvements. A simulation model for the vehicle and another for the liquid cargo were developed, then coupled using the External Force principle. Validation tests were carried out on a real vehicle. Two publications have resulted. | |
| Studying the dynamic behavior of motorcycles is a tricky business, since it's not very stable without corrective action on the part of the rider.
Another reason why the "2-wheel" sector is less well known than the "4-wheel" sector is that the motorcycle industry is significantly smaller than the automotive sector. The aim of the work presented here is to quantify the deceleration potential of a motorcycle according to its geometry. Starting from top right: rev counter, gear engaged on white background, speedometer bar for gas pedal, brake and clutch position handlebar position the red figure at top left is the instantaneous value of the accelerometer linked to the suspended mass. Text with numerical values for time, distance and speed On a grey background, the bars show the tire's longi (green) and lateral (red) load rates: the front end is not saturated. |
|
| The corrugated sheet test at a fixed wavelength, but run at progressively increasing speed; you can clearly see the quiet zone, resonance, then filtration, with all the non-linearities (wheel detachment, loss of traction, compression stop...). | |
| The tractor-trailer convoy is a test bed for jumbo jet tires, placed in the center of the trailer; when the wheel is steered progressively, it generates a lateral thrust that disturbs the balance of the convoy. |
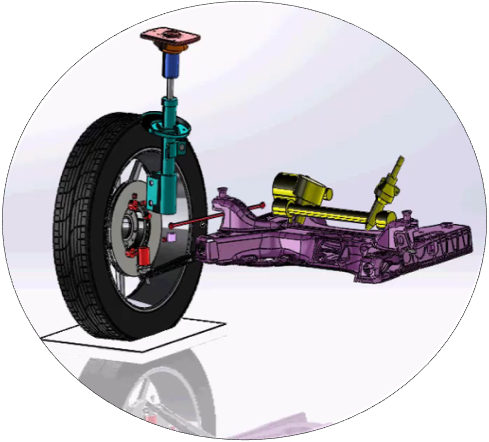
Kinematics
 |
LIS and LECOS are suspension design software packages whose essential originality lies in the fact that, in addition to the ability to calculate directly from (suspension) points to the wheel's kinematic curves in terms of travel and steering, they are able to back-solve from the desired characteristics to the free values of the points' coordinates, i.e. design to functional specification. |